How a pH Meter Works – Advantages and Uses
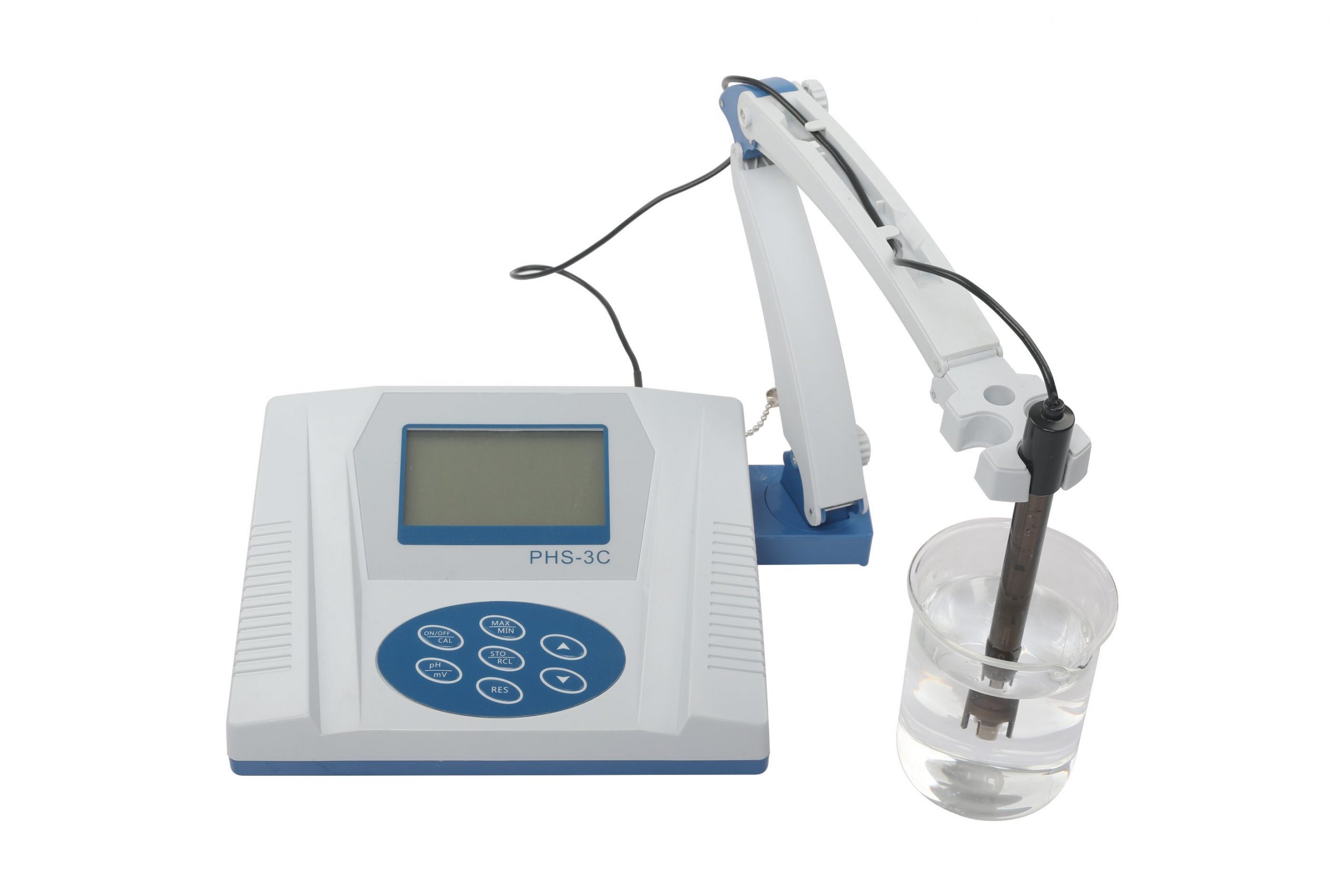
A pH meter, also known as a pH monitor, is a non-invasive scientific instrument which measures the alkalinity or acidity of water through its electrodes. This type of meter can be used to measure the pH of body fluids and blood samples. It can also be used to identify the presence of medication or any other bio-chemical that may be present in human or animal blood or urine. It is designed to measure the pH in an area faster than traditional methods. Other applications of a pH meter are in various industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and industrial cleaning. This meter has several advantages over other pH testing methods.
Advantages of pH Meter
The advantages of using pH meters in the laboratory are that it is fast and inexpensive. pH testing requires manual measurement of various concentrations of pH using test strips, diluators and pH containers. The accuracy of these methodologies depends greatly on the materialization of various sized bubbles on the external surface of the material being tested. In addition, certain types of membranes may not provide an accurate reading even with the use of special pH test strips. Using pH meters in the laboratory eliminates the need for manual measurement of pH in an area where a large concentration of dissolved substances could be present.
Another advantage of using a pH meter in the laboratory is that it is less sensitive to extraneous contamination compared to other pH measuring methods. Most laboratory tests and measurements rely on the ability of a specific chemical or biological contamination to interact with a specific pH substance. Contamination of the instrument with foreign bodies may introduce errors into the calibration. pH measurements therefore depend much on the calibration of the equipment and its chemistry.
Factors
Several factors affect the performance of a pH meter. These factors are equilibrium, ionization, and the ratio of alkalinity and acidity. These four factors are very sensitive to changes in other factors such as temperature, batch size, and relative humidity. The overall performance of the pH meter depends on the understanding and calibration of several other physical, chemical, and biological properties of the solution used as a substrate for measurement.
Indicators
Some pH testers are equipped with indicators that can indicate several different pH values, which is useful for laboratory personnel in their daily work. It can also be used by pharmacists to determine the acidity or alkalinity of a patient’s blood. This enables pharmacists to prescribe different remedies based on the acidity of the patients’ bloodstream. PH meters can also be used in clinical laboratories. Because several conditions can affect the production or release of pH value, ph meters are used in conjunction with various techniques for determining these parameters.
When determining the concentration or percentage of alkalinity or acidity in a liquid or thick mixture, several variables must be considered. First, the sample must be subjected to the external environment. Second, the sample must be kept at a specific temperature so that its properties can be measured effectively. And third, the external environment must provide the right conditions for the pH meter to function properly.
Ph measure devices based on electronic technology have revolutionized the laboratory. These instruments can measure the pH level of a substance in a matter of seconds. Before this technological innovation, it took a scientist several hours or even days to determine the chemical equilibrium of a sample. Modern chemistry laboratories all over the world now rely on pH meters as a means of measuring the acid/alkaline content of samples. In the process, they gain valuable knowledge about the chemical processes taking place in nature.
Uses of pH Meter
A pH meter can either be used for general purpose or sensitive applications. General purposes include medical laboratory testing, industrial cleaning, pharmaceutical applications, and water testing. Sensitive applications are used for the analysis of the atmosphere, human body, food products, and some liquids. When purchasing a pH meter for your laboratory, always ask if it can measure the in a matter of seconds, whether it uses batteries or AC.