How To Treat Cardiac Tamponade – Cure Cardiac Paradoxus
Symptoms
A patient with pulsus paradoxus often experiences two distinct symptoms: chest pain and a sensation of breathlessness. In the case of chest pain, the patient has at first no idea that he/she is having a cardiac problem. In the second stage of the disease, the patient begins to experience breathlessness. As the disease progresses, the patient can feel dizzy at times, as though they are out of breath. A person with pulsatile heart failure also often feels tightness or soreness in their shoulder, arm, leg, or jaw. In severe cases, pulsatile heart failure can lead to a detached pulmonary artery, resulting in the cessation of oxygenation to the brain.
Chest pain can be caused by the enlargement or relaxation of the interventricular septum. This is where the air/blood flows from the middle to the left side of the heart. The enlargement of the septum can be caused by the accumulation of scar tissue, narrowing of the passages, or other physiological changes. Sometimes, people who suffer from pulsus paradoxus do not experience chest pain, but instead have abdominal pain. The diagnosis of pulsatile heart failure is usually based on the presence of abdominal pain, which is considered to be another symptom of the disorder.
Blood pressure is a function of the force with which blood is forced through the vessels of the heart. As blood flow is decreased, the blood pressure rises. People suffering from pulsus paradoxus have normal blood pressure (which means that there is normal blood flow). However, this condition can increase abruptly (up to ten mmhg) and greatly deplete oxygen from the blood. When the level of oxygen in the blood reaches the critical point, the result is death from ventricular fibrillation (or a heart attack).
Pulsus paraganglum, sometimes called pulsatile or paraxanthin vascular tachycardia, refers to a temporary drop in blood pressure of up to 10mm Hg with every pulse in your body. This is often enough of an appreciable change to cause a marked change in your heart’s pumping strength. It can cause the weakening of the heart muscle and weaken the heart’s ability to pump blood throughout your body. The more readily you can adapt your lifestyle to reduce your pulsating heartbeat, the sooner you will get back to your normal way of living.
Pulmonary Hypertension
People who have suffered from pulsus paradoxus are at risk of developing pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary hypertension is the condition wherein the volume of the fluid in the lungs increases beyond the normal range, causing an increase in the pressure of the blood in the lungs. This condition can occur even in people who are perfectly healthy. Some of the symptoms of pulmonary hypertension include cough with mucus, shortness of breath while sleeping, chronic coughing with no clear end point, coughing that produces a wheezing sound, wheezing more than eight times a week, and chest pains. The condition can progress to more serious conditions such as emphysema and the development of the heart disease heart block.
Cause
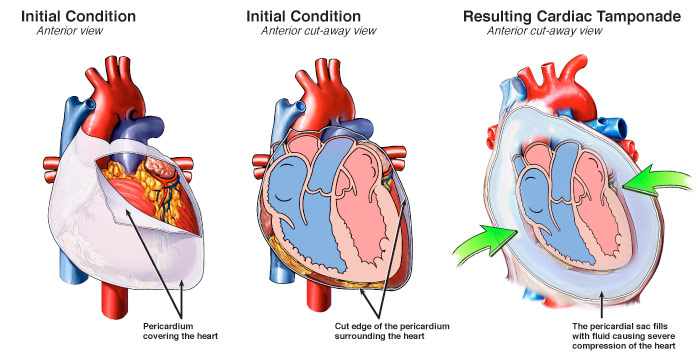
Tearing of the membranes of the heart, or pericardial infarction, is another cause of pulsus paradoxus. This happens when there is a decrease in blood flow to the heart muscle or atrial spasm. Because this causes the heart muscle to contract more severely, the blood is forced back into the pulmonary artery, causing a reduction in the blood flow towards the heart. Cardiac tamponade is a dangerous condition that can lead to the development of heart attack.
People who suffer from pulsus paradoxus can reduce the occurrence of this condition by taking measures which will control high blood pressure. Controlling high blood pressure through diet and drug therapy is effective. These drugs lower the systolic and the diastolic blood pressures. It has been proven that when the systolic blood pressure is reduced by 10 mmHg, the probability of cardiac arrest is reduced by about 70%. However, it is always advised to see a doctor before taking these drugs.
Prevention
The best way to prevent pulsus paradoxus from occurring is to make sure you do not take large doses of medicines, and that you avoid taking drugs which can cause blood pressure cuff problems. Drugs which include beta-blockers and diuretics should be avoided. A good example would be aspirin. Medications that contain inhaled corticosteroids are also known to aggravate this condition. Smoking should be quit as soon as possible.